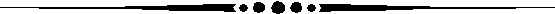Gaerttner LINAC Receives ANS Landmark
Award
From the June 1998 Nuclear News--"For over 35 years of generating accurate data for nuclear
reactor designs, the Gaerttner LINAC Laboratory at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute was
awarded a Nuclear Historic Landmark Award by ANS. The high-power electron linear
accelerator has served government as well as industry applications since the early 1960s, and was
one of the first to provide intense pulsed beams of neutrons for time-of-flight experiments."
Robert Block, current director of the laboratory, accepted the award from Ted Quinn, ANS
president-elect and RPI alumnus, in an April 3 ceremony hosted by the ANS Eastern New York
Section and RPI.
During its many years of operation, the Gaerttner LINAC Laboratory conducted measurements of
neutron thermalization, neutron cross-sections on both stable and radioactive isotopes, neutron
spectra from large pulsed assemblies, photoneutron production, radiation effects in components,
and the effects of intense radiation in microelectronics. The plutonium-239 alpha measurements
carried out jointly with the Oak Ridge National Laboratory showed that the steam-cooled
intermediate spectrum breeder concept would not be practical because of the high alpha
measured in this energy range. "As a result, the breeder program shifted its focus exclusively to
the liquid-sodium-cooled LMFBR design. Numerous measurements were carried out in support
of the LMFBR, as well as for thermal reactors, and today there is a strong program in low-energy
cross-section measurements."
We in the Radiation Safety Information Computational Center have enjoyed a long reciprocal
relationship with the staff and students of RPI. We congratulate those who have and are
operating the Gaerttner LINAC Laboratory on receiving this award. If you wish to learn more
about the Gaerttner LINAC Laboratory you will find additional information at
http://www.linac.rpi.edu/
CHANGES TO THE COMPUTER CODE
COLLECTION
Four changes or additions were made to the computer code collection during the month. Three
new code systems were packaged and added to the collection, and one code system was
corrected. Two changes resulted from foreign contributions.
 Oak Ridge National Laboratory contributed a replacement for the
MORSE portion of this Monte Carlo code system for the design and
analysis of calorimeter systems, Spallation Neutron Source (SNS) target
systems, etc. CALOR95 was designed to assist experimentalists evaluate
and analyze different types of calorimeter systems used in many
high-energy physics experiments to determine the energy and direction of
incident hadrons, leptons, and photons. The code package contains HETC95, SPECT95, EGS4,
MORSE, and other support programs. The MORSE version in earlier releases of CALOR95 did
not yield the correct energy balance because absorbed gamma-ray energies were underestimated.
Oak Ridge National Laboratory contributed a replacement for the
MORSE portion of this Monte Carlo code system for the design and
analysis of calorimeter systems, Spallation Neutron Source (SNS) target
systems, etc. CALOR95 was designed to assist experimentalists evaluate
and analyze different types of calorimeter systems used in many
high-energy physics experiments to determine the energy and direction of
incident hadrons, leptons, and photons. The code package contains HETC95, SPECT95, EGS4,
MORSE, and other support programs. The MORSE version in earlier releases of CALOR95 did
not yield the correct energy balance because absorbed gamma-ray energies were underestimated.
CALOR95 runs on IBM RS/6000 computers and requires the XLF Fortran 77 compiler. It is
transmitted on either one CD-ROM, DC 6150 (150 MB), 4-mm DAT (8GB), or 8-mm (2.3GB)
cartridge tape in compressed UNIX tar format. References ORNL/TM-11185 (unpublished
report) and SDC-92-00257 (May 1992). Fortran 77; IBM RS/6000 (C00610/IRISC/01).
 The Faculty of Physics and Nuclear Techniques, University of Mining
and Metallurgy, Cracow, Poland, contributed a new code system for
one-dimensional transport and burnup calculations. In BISON-C the
one-dimensional transport equation is solved by the discrete ordinates
method with anisotropic scatterings. Bateman's method is adopted to
solve the production-depletion equations for burnable nuclides. A burnup
calculation is carried out by performing these two processes iteratively.
The Faculty of Physics and Nuclear Techniques, University of Mining
and Metallurgy, Cracow, Poland, contributed a new code system for
one-dimensional transport and burnup calculations. In BISON-C the
one-dimensional transport equation is solved by the discrete ordinates
method with anisotropic scatterings. Bateman's method is adopted to
solve the production-depletion equations for burnable nuclides. A burnup
calculation is carried out by performing these two processes iteratively.
The BISON-C system was based on CCC-464/BISON 1.5, which was based on
CCC-254/ANISN-ORNL. The new code system extends the original code by providing burnup
calculation for fission products and other features like differentiation of time steps and burnup
normalization to the required thermal power. The new burnup library, based on JENDL-3,
additionally contains the fission product burnup chain and the fission yields for actinides
prepared from ENDF-B/VI data files. Included is a cross-section library processing system which
is comprised of XSCON, RESPL, and SIGC. BISON-C runs on Unix-based operating systems on
IBM RS/6000 and HP and requires a Fortran 77 compiler. It is transmitted on 2 DS/HD diskettes
in a compressed Unix tar file. Reference: INT 271/I (1997). Fortran 77; IBM RS/6000 and HP
(C00659/MNYWS/00).
 Argonne National Laboratory-West, Idaho Falls, Idaho, contributed this
computer code system for generalized least-squares evaluation of related
cross sections for ENDF/B based on Gauss, Markov, and Aitken. The
simultaneous evaluation of the interrelated cross section data of 6Li(n,),
6Li(n,n), 10B(n,0), 10B(n,1), 10B(n,n), 197Au(n,), 238U(n,), 235U(n,f), 239Pu(n,f), 238U(n,f) and the
thermal constants was part of the evaluation of these data for ENDF/B-VI. The Fortran codes and
the data files used for the simultaneous evaluation are included in this package. This
experimental data analysis code system, known as GMA, utilizes the generalized least-squares
estimation method. Associated codes included are RCL (which is used to edit, list and expand the
basic data file) and DAT (which is used to reduce the cross section data to a common energy
grid.)
Argonne National Laboratory-West, Idaho Falls, Idaho, contributed this
computer code system for generalized least-squares evaluation of related
cross sections for ENDF/B based on Gauss, Markov, and Aitken. The
simultaneous evaluation of the interrelated cross section data of 6Li(n,),
6Li(n,n), 10B(n,0), 10B(n,1), 10B(n,n), 197Au(n,), 238U(n,), 235U(n,f), 239Pu(n,f), 238U(n,f) and the
thermal constants was part of the evaluation of these data for ENDF/B-VI. The Fortran codes and
the data files used for the simultaneous evaluation are included in this package. This
experimental data analysis code system, known as GMA, utilizes the generalized least-squares
estimation method. Associated codes included are RCL (which is used to edit, list and expand the
basic data file) and DAT (which is used to reduce the cross section data to a common energy
grid.)
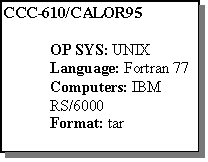
GMA runs on UNIX operating systems on Sun and IBM RS/6000 workstations and on personal
computers. Executables created with the LAHEY F77L3/EM-32 5.2 compiler are included to run
on PCs in a DOS window of Windows95. The package is transmitted on 2 DS/HD diskettes in
both UNIX and DOS compressed formats. References: ANL/NDM-139, (ENDF-358)(1997).
Fortran 77, Fortran 90; Pentium-based PC, and Sun and IBM RS/6000 workstations
(P00367/MNYCP/00).
 The Department of Nuclear Reactions at Moscow State University,
Russia, contributed this code system designed for quick and easy
estimations of basic stopping characteristics of proton transmission for
generation of the source definition (SDEF) portion of the input data for
MCNP. It does not generate the full MCNP input file. The
MSM-SOURCE code generates the input data for the MCNP code (for 3b
and 4 versions), simulating the set of single neutron sources, produced in the sample during the
proton transmission. It permits one to extend the possibilities of the MCNP code for
consideration of secondary neutrons from the proton interaction with nuclei of the sample
substance. The MSM-SOURCE code is applicable for calculations of the proton transport for the
incident energies from 0.1 to 1 GeV and various targets 12 < A < 238.
The Department of Nuclear Reactions at Moscow State University,
Russia, contributed this code system designed for quick and easy
estimations of basic stopping characteristics of proton transmission for
generation of the source definition (SDEF) portion of the input data for
MCNP. It does not generate the full MCNP input file. The
MSM-SOURCE code generates the input data for the MCNP code (for 3b
and 4 versions), simulating the set of single neutron sources, produced in the sample during the
proton transmission. It permits one to extend the possibilities of the MCNP code for
consideration of secondary neutrons from the proton interaction with nuclei of the sample
substance. The MSM-SOURCE code is applicable for calculations of the proton transport for the
incident energies from 0.1 to 1 GeV and various targets 12 < A < 238.
This code is based of the Moving Source Model (MSM) and Bethe stopping theory with the
relativistic corrections for protons. It allows the estimations of the proton range, the changes of
the proton current and the neutron production versus the depth. The double differential spectra
and the multiplicities of nucleons, produced in the primary proton-induced reactions, are
obtained.
MSM-SOURCE runs on many computers including personal computers and IBM RS/6000 under
either DOS or UNIX. It has been compiled with Microsoft Fortran 5.1, WatCom Fortran,
NDP-Fortran, and Lahey compilers on PC. The Lahey Fortran 90 V4.5 compiler was used to
create the executable included in the package which is transmitted on one DS/HD (1.44MB)
diskette written in DOS format. References: README.TXT (May 1998). Fortran 77; PC 386 or
higher processor, IBM RS/6000 (P00369/MNYCP/00).
CONFERENCES, COURSES, SYMPOSIA
RSICC attempts to keep its users/contributors advised of conferences, courses, and symposia in
the field of radiation protection, transport, and shielding through this section of the newsletter.
Should you be involved in the planning/organization of such events, feel free to send your
announcements and calls for papers via email to raf@ornl.gov.
FLINS'98
The Third International FLINS Workshop on Fuzzy Logic and Intelligent Technologies for
Nuclear Science and Industry organized by the Belgian Nuclear Research Centre ( SCKCEN)
will be held September 14-16, 1998, at the Astrid Park Plaza Hotel in Antwerp, Belgium. FLINS,
an acronym for Fuzzy Logic and Intelligent technologies in Nuclear Science, is an international
research forum which endeavors to advance the theory and applications of fuzzy logic and novel
intelligent technologies in nuclear science and industry.
Following FLINS'94 and FLINS'96, the first and second international workshops on this topic,
FLINS'98 aims to bring together scientists, researchers, and people from industry to introduce the
principles of intelligent systems and soft computing such as fuzzy logic (FL), neural network
(NN), genetic algorithms (GA) and any combinations of FL, NN, and GA, knowledge based
expert systems and complex problem solving techniques within nuclear industry and related
research fields.
FLINS'98 offers a unique international forum to present and discuss new and useful techniques
for nuclear science and industry. Contact: Dr. Da Ruan, FLINS'98 Chair, SCKCEN-FLINS,
Nuclear Research Centre, Boeretang 200, B - 2400 Mol, Belgium (phone 32-14-33-2272, fax:
32-14-32-1529, email druan@sckcen.be). Additional information may be found at
http://www.sckcen.be/conferences/flins_ 98.html.

The Second International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Applications of Accelerator Technology
(AccApp'98) is sponsored by the Accelerator Applications Technical Group of the American
Nuclear Society (ANS), and is hosted by the Oak Ridge-Knoxville, Tennessee, Section of the
ANS. It will be held in Gatlinburg, Tennessee, during the week of September 20-23, 1998, at the
Park Vista Hotel & Conference Center. AccApp'98 will provide a forum for discussion of the
uses of particle accelerator technology for nuclear applications. It will focus on production of
neutrons and other particles, utilization of these particles for scientific or industrial purposes,
production or destruction of radionuclides significant to energy, medicine, defense, or other
endeavors, as well as imaging and diagnostics. Relevant information is located at
http://www.engr.utk.edu/org/ans/AccApp98.
21st RERTR
The 21st International Meeting on Reduced Enrichment for Research and Test Reactors
(RERTR) will be held October 18-23, 1998, in São Paulo, Brazil. Information will be exchanged
on the progress of national and international programs to develop low enriched fuels for research
and test reactors and to convert the reactors to such fuels. This meeting is organized by the
Institute of Research and Development Directorate of the Brazilian Nuclear Energy Commission
(CNEN) (IPEN) in cooperation with the International Atomic Energy Agency, Argonne National
Laboratory, the Brazilian Nuclear Energy Commission, the Brazilian Association for Nuclear
Energy (ABEN), and other sectors of the Brazilian nuclear energy industry. Further information
about the meeting is available from Dr. José Rubens Maiorino, Chairman 1998-RERTR Meeting,
Comissão Nacional de Energia Nuclear, Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares, Diretoria
de Reatores, Travessa R 400 - Cidade Universitária- CEP: 05508-900, São Paulo - SP - Brazil
(phone 55-11-) 816-9111, fax 55-11-816-9432, email rertr98@net.ipen.br), or please visit the
webpage at url http://www.ipen.br/r/rertr/rertr.html).
CIRMS
The Seventh Annual Meeting of the Council on Ionizing Radiation Measurements and Standards
(CIRMS) will be held at the National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg,
Maryland, October 19-21, 1998. CIRMS is a non-profit, U.S. Council, with representation from
academic, professional and industrial associations and organizations, government agencies and
interested individuals. CIRMS provides an opportunity for open discussion of current issues
concerning ionizing radiation and future directions of measurements and standards. For more
information contact Katy Nardi, (phone 770-622-0026, email KatyNardi@aol.com).
Tenth International Symposium on Reactor Dosimetry
The Tenth International Symposium on Reactor Dosimetry will be held September 12-17, 1999,
in Osaka, Japan. This Symposium is held about every three years to provide a forum for the
interchange of state-of-the-art techniques, databases and standardization of radiation metrology.
The Symposium will be of value to those involved in reactor dosimetry, including researchers,
manufacturers and representatives from industry, utilities and regulatory agencies. The
Symposium is jointly sponsored by the Atomic Energy Society of Japan (AESJ), the American
Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) and the European Working Group on Reactor
Dosimetry (EWGRD). It is organized by ASTM Committee E10 on Nuclear Technology and
Applications and EWGRD.
The Symposium theme is dosimetry for the assessment of irradiated reactor materials and reactor
experiments, featuring radiation metrology techniques, databases and standardization. Inquiries
and requests to be added to the mailing list should be sent to one of the of the following:

"Half a Century of Radiation Shielding Research and Its Evolution into the Next Era" is the
theme for the 9th International Conference on Radiation Shielding to be held October 17-22,
1999, in Tsukuba, Japan. It is sponsored and organized by the Japan Atomic Energy Research
Institute and co-sponsored by the OECD-Nuclear Energy Agency-Nuclear Science Committee
(NEA-NSC), Atomic Energy Society of Japan (AESJ), and the Radiation Safety Information
Computational Center (RSICC). Participants in the conference explore the scientific,
technological and engineering issues associated with radiation shielding in broad nuclear energy
systems, accelerator facilities, space and general environments. Detailed information about the
conference may be obtained from Yujiro Ikeda, Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute, Tokai
Research Establishment, Neutron Science Research Center, Spallation Neutronics Laboratory,
Tokai-mura, Naka-gun, Ibaraki-ken 319-11 Japan (phone 81-29-282-6074, fax 81-29-282-5709,
email keda@fnshp.tokai.jaeri.go.jp) or from the web page at http://icrs9.tokai.jaeri.go.jp.

Calendar
Your attention is directed to the following events of interest.
September 1998
AccApp'98, Sept. 20-23, 1998, Gatlinburg, Tennessee, sponsored by the Oak Ridge-Knoxville, TN, USA Section of the
ANS. Contact: Dr. John Haines, Chairman, AccApp '98 Technical Program Committee, Oak Ridge National Laboratory,
Oak Ridge, TN 37831-8071, USA (phone 423-574-0966, fax 423-576-7926, email hainesjr@ornl.gov, url
http://www.engr.utk.edu/org/ans/AccApp98)
Training Course on the Use of MCNP in Radiation Protection and Dosimetry, Sept. 28-1 Oct. 1998, at the Imperial
College of Science, Technology and Medicine, London. Contact: Robert Alan Price, Imperial College of Science,
Technology and Medicine, T. H. Huxley School of the Environment, Earth Sciences and Engineering, Applied Modelling
and Computation Group, Centre for Environmental Technology, Room 405, Royal School of Mines Building, Prince
Consort Rd, London SW7 2BP, UK (phone 44-171-594- 9323, fax 44-171-594-9341, url
http://wrench.et.ic.ac.uk/courses/).
October 1998
4th Annual Workshop on Monte Carlo Simulation of Radiotherapy Treatment Sources using the OMEGA/BEAM Code
System, Oct. 5-8, 1998, Ottawa, Canada. Contact: Blake Walters, Ionizing Radiation Standards, National Research
Council of Canada, Ottawa, Canada, K1A 0R6. (phone 613-993-2715, fax 613-952-9865, email bwalters@irs.phy.nrc.ca,
url www.irs.inms.nrc.ca/inms/irs/BEAM/ beamhome.html)
21st International Meeting on Reduced Enrichment for Research and Test Reactors (RERTR) Oct. 18-23, 1998, São
Paulo, Brazil. Contact: Dr. José Rubens Maiorino, Chairman 1998-RERTR Meeting, Comissão Nacional de Energia
Nuclear, Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares, Diretoria de Reatores, Travessa R 400 - Cidade Universitária-
CEP: 05508-900, São Paulo - SP - Brazil (phone 55-11-816-9111, fax 55-11-816-9432, email rertr98@net.ipen.br; url
http://www.ipen.br/r/rertr/rertr.html).
7th Annual Meeting of the Council on Ionizing Radiation Measurements and Standards (CIRMS) Oct. 19-21, 1998,
NIST, Gaithersburg, Maryland. Contact: Katy Nardi, (770-622-0026, email KatyNardi@aol.com).
November 1998
Radiation Safety Officer, Nov. 2-6, 1998, Las Vegas, Nevada, a Technical Short Course offering of Nevada Technical
Associates. Contact: Nevada Technical Associates, Inc., P.O. Box 90748, Henderson, NV 89009 (phone 702-564-2798,
fax 702-558-7672).
April 1999
First Latin American Symposium on Nuclear Tracks and Radiation, April 5-9, 1999, Caracas, Venezuela, Institute for
Advanced Studies, Convention Centre. Contact: Professor Laszlo Sajo, Universidad Simon Bolivar, FE-1, Apdo 89000,
Caracas, Venezuela, (phone 58-2-906- 3590, fax 58-2-906-3712, email lsajo@fis.usb.ve).
June 1999
Conference on Radionuclide Metrology and its Application, June 7-11, 1999, Prague. Contact: Pavel Dryák, Czech
Metrological Institute, Radiova 1, CZ 102 00 Prague, Czech Republic (phone 420-2-67008244, fax 420-2-67008466,
email pdryak@cmi.cz).
September 1999
Tenth International Symposium on Reactor Dosimetry, Sept. 12-17, 1999, in Osaka, Japan. Contact: Dr. David W. Vehar
(505-845-3414, fax 505-844-0798, email: dwvehar@sandia.gov) or Dr. Hamid Ait Abderrahim (32-14-332277, fax 32-
14-321529, email haitabde@sckcen.be).
October 1999
Half a Century of Radiation Shielding Research and Its Evolution into the Next Era (ICRS-9) Oct. 17-22, 1999, Tsukuba,
Japan, sponsored and organized by the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute. Contact: Yujiro Ikeda, Japan Atomic
Energy Research Institute, Tokai Research Establishment, Neutron Science Research Center, Spallation Neutronics
Laboratory, Tokai-mura, Naka-gun, Ibaraki-ken 319-11 Japan (phone 81-29-282-6074, fax 81-29-282-5709, email
keda@fnshp.tokai.jaeri.go.jp, url http://icrs9.tokai.jaeri.go.jp.
JUNE ACCESSION OF LITERATURE
The following literature cited has been reviewed and placed in the RSICC Information Storage
and Retrieval Information System (SARIS), now searchable on the RSICC web server
(http://www-rsicc.ornl.gov/SARIS.html). This early announcement is made as a service to the
shielding community. Copies of the literature are not distributed by RSICC. They may
generally be obtained from the author or from a documentation center such as the National
Technical Information Service (NTIS), Department of Commerce, Springfield, Virginia 22161.
For literature listed as available from INIS contact INIS Clearinghouse, International Atomic
Energy Agency, P.O. Box 100, A-1400 Vienna.
RADIATION SHIELDING LITERATURE
ORNL/TM-13170/V2 . . . Characteristics of Spent Fuel from Plutonium Disposition Reactors Vol. 2: A General Electric
Boiling-Water-Reactor Design. . . . Ryman, J.C.; Hermann, O.W. . . . April 1998 . . . Oak Ridge National Laboratory,
Oak Ridge, TN.
Nucl. Technol., 122, 255-264 . . . Criticality Analysis of the Multiplying Material Inside the Chernobyl Sarcophagus. . . .
Maucec, M.; Ravnik, M.; Glumac, B. . . . June 1998 . . . Jozef Stefan Institute, Ljubljana, Slovenia.
Nucl. Technol., 122, 276-283 . . . Fission Gas Release Determination Using an Anti-Compton Shield Detector. . . .
Matsson, I.; Grapengiesser, B.; Jansson, P.; Hakansson, A.; Backlin, A. . . . June 1998 . . . ABB Atom AB, Vasteras,
Sweden; Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden.
Nucl. Technol., 122, 306-317 . . . A Structured Methodology for Waste Management Facility Accident Analysis. . . .
Mueller, C.J.; Folga, S.M.; Roglans-Ribas, J.; Nabelssi, B.; Mishima, J. . . . June 1998 . . . Argonne National Laboratory,
Argonne, IL; Science Applications International Corp., Richland, WA.
Nucl. Technol., 122, 330-354 . . . Nuclear Applications of Accelerator-Driven Spallation Targets. . . . Van Tuyle, G.J. . .
. June 1998 . . . Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY.