 |
Oak Ridge National Laboratory Post Office Box 2008 Oak Ridge, Tennessee 37831-6362 Managed by UT-Battelle, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy under contract DE-AC05-00OR22725 Phone No. 865-574-6176 |
| No. 422 | March 2000 |
| The spirit of man is more important than mere physical strength, and the spiritual fiber of a nation than its wealth.--Dwight D. Eisenhower | |
- UT-Battelle Takes the Reins
- Area Code Changes for RSICC
- NRC Codes Made Available
- CHANGES TO THE COMPUTER CODE COLLECTION
- CHANGES TO THE DATA LIBRARY COLLECTION
- Obituary
- CONFERENCES, COURSES, SYMPOSIA
- PHYSOR Workshops
- What's New With DOORS
- New Capabilities in MCNP4C
- PENTRAN 3-D Parallel Sn (PSU)
- Automated Variance Reduction with A3MCNP for Shielding Problems (PSU)
- Practical MCNP for the Health /Medical Physicist & Rad Engineer
- MCNP and Visual Editor Training Course
- MCNP Workshops for the Year 2000
- Reactor Analysis and Criticality Safety Short Courses
- SNA 2000
- MC2000
- Calendar
UT-Battelle Takes the Reins
April 1, 2000, was the official start date of the UT-Battelle contract with the U. S. Department of Energy to operate Oak Ridge National Laboratory. New Laboratory Director, Bill Madia, had this to say on the occasion:
| "This is an exciting day for me and the members of the UT-Battelle
leadership team. We are honored to begin a partnership with the
Department of Energy and the outstanding staff at Oak Ridge
National Laboratory. The partnership is one we believe will be
mutually beneficial for years to come. ORNL is one of the world's
finest research and development facilities. Working with you and
the Department of Energy, UT-Battelle's goal will be to enhance the
Lab's capabilities and improve the quality of life for its employees.
The transition period served to reaffirm our belief that success will
depend upon achieving simultaneous excellence in science and
technology, laboratory operations and ES&H, and community
service. Based upon what we learned, our agenda for ORNL will
focus on four basic initiatives.
"First, we must pursue every opportunity to grow the Lab's portfolio. Second, we must broaden ORNL's partnerships and be viewed as a highly valued asset among the Lab's stakeholders. Third, we must update the facilities at ORNL if we are to continue to attract and retain world class scientists. Finally, in large and small ways we must reduce the cost of doing business within the Lab. We view each of these initiatives as priorities essential to the Lab's future." |
The Radiation Safety Information Computational Center staff welcomes UT-Battelle, LLC.
Area Code Changes for RSICC
 This is it. Your last chance to change the
programming for your phone calls to
RSICC. The area code for parts of East
Tennessee changed from 423 to 865
effective November 1, 1999. April 24, 2000,
is the last day on which both area codes can be used.
This is it. Your last chance to change the
programming for your phone calls to
RSICC. The area code for parts of East
Tennessee changed from 423 to 865
effective November 1, 1999. April 24, 2000,
is the last day on which both area codes can be used.
NRC Codes Made Available
Several U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) software packages which were transferred from the ESTSC to RSICC were incorporated into the RSICC computer code collection. Please browse the computer code abstracts available at RSICC's www site for more information on these packages.
CCC-524/IRDAM
PSR-482/REMIT 3.5
CHANGES TO THE COMPUTER CODE COLLECTION
Two changes were made to the computer code collection during the month. One new code system was added and one code system was corrected. One change resulted from a foreign contribution.
 Synthesis Srl and ENEL, SpA in Milano, Italy, through the
OECD NEA Data Bank, contributed this code system for best
estimate coupled 3D neutronics-thermalhydraulics
calculations. TRAC-PF1-EN/MOD3 is a combined computer
program comprising a revised version of the TRAC-PF1
transient reactor analysis code and a specially implemented
three-dimensional two-group neutron kinetics code
(QUANDF). Starting from either a critical steady-state or a
subcritical steady-state in a PWR plant, the code allows one
to simulate the neutronic and thermal-hydraulic core transient response to reactivity
accidents initiated both inside and outside the vessel.
Synthesis Srl and ENEL, SpA in Milano, Italy, through the
OECD NEA Data Bank, contributed this code system for best
estimate coupled 3D neutronics-thermalhydraulics
calculations. TRAC-PF1-EN/MOD3 is a combined computer
program comprising a revised version of the TRAC-PF1
transient reactor analysis code and a specially implemented
three-dimensional two-group neutron kinetics code
(QUANDF). Starting from either a critical steady-state or a
subcritical steady-state in a PWR plant, the code allows one
to simulate the neutronic and thermal-hydraulic core transient response to reactivity
accidents initiated both inside and outside the vessel.
The present version of TRAC-PF1-EN/MOD3 is intended for use on a personal computer but, with some changes, it has also been tested on a UNIX workstation (IBM Power PC-RISC system 6000/250) and on a mainframe (IBM system 9021/832). The MS Fortran Power Station Compiler version 1.0 or higher can be used under DOS 6.0 or WINDOWS 95. The Digital Visual Fortran v.5.0 was used to create an executable included in the package. The package is transmitted on CD-ROM which contains the Fortran source files and executable, code manual, and the input/output files for the three sample problems in a self-extracting, compressed DOS file. Reference: Rep. 1037/3 (February 1997). Fortran 77; PC 486 (P00477PC48600).
 Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico,
contributed a new version of this code system for producing
pointwise and multigroup neutron and photon cross sections
from ENDF/B data. NJOY is a modular computer code used
for converting evaluated nuclear data in the ENDF format into
libraries useful for applications calculations. Because the
Evaluated Nuclear Data File (ENDF) format is used all around
the world (e.g., ENDF/B-VI in the U.S., JEF-2.2 in Europe,
JENDL-3.2 in Japan, BROND-2.2 in Russia) NJOY allows access to a wide variety of
the most up-to-date nuclear data. NJOY99 is a cleaned up version of NJOY 97.107 that
features improved consistency between different systems, more use of block
structures, a consistent set of physical constants and support for the
CCC-700/MCNP4C Monte Carlo Program, which will soon be released.
Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico,
contributed a new version of this code system for producing
pointwise and multigroup neutron and photon cross sections
from ENDF/B data. NJOY is a modular computer code used
for converting evaluated nuclear data in the ENDF format into
libraries useful for applications calculations. Because the
Evaluated Nuclear Data File (ENDF) format is used all around
the world (e.g., ENDF/B-VI in the U.S., JEF-2.2 in Europe,
JENDL-3.2 in Japan, BROND-2.2 in Russia) NJOY allows access to a wide variety of
the most up-to-date nuclear data. NJOY99 is a cleaned up version of NJOY 97.107 that
features improved consistency between different systems, more use of block
structures, a consistent set of physical constants and support for the
CCC-700/MCNP4C Monte Carlo Program, which will soon be released.
NJOY99 runs on many computers. Machine-specific updates are included for Cray, Sun, IBM RS/6000, SGI Origen 2000, and DEC Alpha workstations, plus Linux and DOS updates for PC. This version was tested on a Sun Ultra in 32-bit mode using f77 and f90, on a Pentium III using linux g77 and Portland Group, Inc. Fortran, on a SGI Origen 2000 using f90, and on a Pentium III under DOS with Lahey LF95 and Absoft compilers. UPD and NJOY99 executables created with the Lahey F95 v5.5d compiler under WindowsNT 4 are included in the package. All Unix systems require a Fortran compiler. The distribution includes the NJOY99 and UPD source codes, PC executables, updates, makefiles, selected ENDF/B data sets for test cases, sample problem input and output. The package is transmitted on CD-ROM in both tar and DOS formats. References: "README0" (December 31, 1999), LA-12740-M (October 1994), LA-12639-MS (ENDF 356) (March 1994), LA-12057-MS (April 1991). Fortran 90 or Fortran 77; Cray, Sun, IBM RS/6000, PC/Linux, PC/DOS (P00480/MNYCP/00).
CHANGES TO THE DATA LIBRARY COLLECTION
One new data library was added to the collection during the month.
 Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee,
contributed this package to compute radiological decay and
daughter ingrowth using the DLC-172/NUCDECAY data
library. The utility code DecayCalc extracts the decay data
from the library for radionuclide(s) specified by the user and
computes the activities of radionuclides present after decay
and ingrowth over a user-specified time period from 1 minute
to 50 years. Decay data for any decay chain may be displayed and printed either in
tabular form or graphically. Radionuclide information is available through the help
system, including decay tables and graphics and dose factors. DecayCalc, in a slightly
modified version, will be a part of CCC-553/Rascal V3 to be released later this year.
Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee,
contributed this package to compute radiological decay and
daughter ingrowth using the DLC-172/NUCDECAY data
library. The utility code DecayCalc extracts the decay data
from the library for radionuclide(s) specified by the user and
computes the activities of radionuclides present after decay
and ingrowth over a user-specified time period from 1 minute
to 50 years. Decay data for any decay chain may be displayed and printed either in
tabular form or graphically. Radionuclide information is available through the help
system, including decay tables and graphics and dose factors. DecayCalc, in a slightly
modified version, will be a part of CCC-553/Rascal V3 to be released later this year.
The unabridged data used in preparing ICRP Publication 38 are distributed in electronic form in this package. The collection consists of data on the energies and intensities of radiations emitted by the 825 radionuclides reported, although abridged, in ICRP Publication 38 plus an additional 13 radionuclides evaluated during preparation of a monograph for the Medical Internal Radiation Dose (MIRD) Committee of the Society of Nuclear Medicine.
DecayCalc is a Windows application that runs under Microsoft Windows 95 or 98, or Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 or later. The Compac Fortran 77 compiler was used to compile the code. The full source for DecayCalc is not provided but will be distributed when Rascal v3 is released.
Included are the referenced document and a CD written in Windows format which includes the data library, the installation code, and the utility code. Reference: Informal user guide (March 2000). Fortran; Pentium running Windows 95/98/NT (D00202PC58600).
Obituary
RSICC has lost many friends and colleagues within the international radiation shielding community. However, it is with great sadness that we report the death of one of our own.
| Constance Marie Anthony, 72, of Oak Ridge, died Thursday, March 30, 2000, at her home. Marie began her association with RSIC (Radiation Shielding Information Center; now RSICC) in 1969 as an information specialist. She retired from the Center in 1990. In the intervening years she managed the testing and packaging of pending codes/data systems and the reproduction of the codes/data documentation. |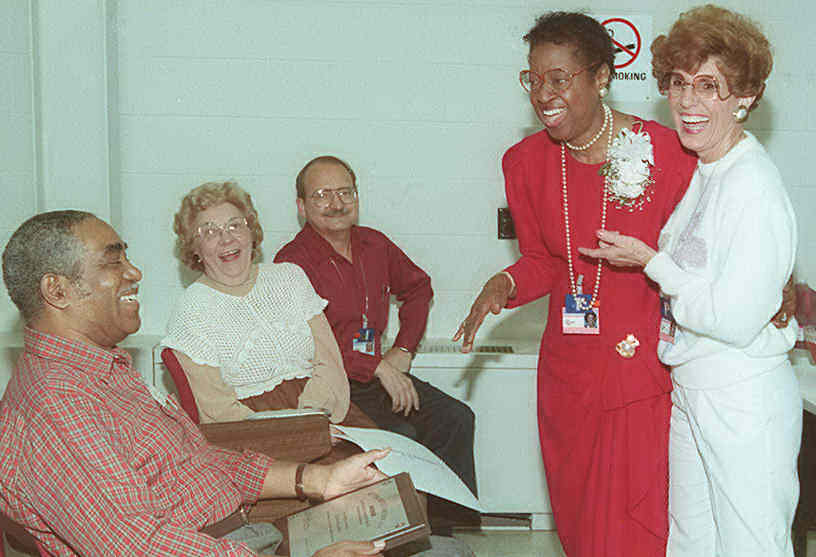 
Marie at her retirement party with, from left to right: husband, William, Henrietta Hendrickson, Robert Roussin, Marie, and her "twin sister" Carol Coker. |
The following are excerpts from Marie's obituary:
Born June 25, 1927 in Nashville, she was the daughter of Albert and Emma C. Hyde Bell. She worked briefly as a teacher in Georgia before coming to Oak Ridge in the early 1950s. Prior to her work at ORNL, she taught kindergarten and third grade at the old Scarboro Elementary School and was an adult education instructor at Oak Ridge High School and ORNL. She also previously worked at ORTEC. Mrs. Anthony was a co-founder of Spurgeon Chapel AME Zion Church in Oak Ridge, where she played the piano and organ for the church choir. She is survived by two sons, Darryl Anthony and his wife, Deborah, and Michael Anthony and his wife, Melissa; a daughter, Denise Anthony; and four grandchildren. Her husband, William Bright Anthony, died Aug. 25, 1992.
CONFERENCES, COURSES, SYMPOSIA
RSICC attempts to keep its users/contributors advised of conferences, courses, and symposia in the field of radiation protection, transport, and shielding through this section of the newsletter. Should you be involved in the planning/organization of such events, feel free to send your announcements and calls for papers via email to raf@ornl.gov with "conferences" in the subject line. Please include the announcement in its native format as an attachment to the message. If the meeting is on a website, please include the url.
Every attempt is made to ensure that the links provided in the Conference and Calendar sections of this newsletter are correct and live. However, the very nature of the web creates the possibility that the links may become unavailable. In that case, please call or mail the contact provided.
PHYSOR Workshops
The following workshops which are co-sponsored by RSICC will be offered at the
upcoming PHYSOR 2000 meeting, May 7-11, in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.
A half-day workshop on recent advances in ORNL's discrete ordinates transport
code system (DOORS) will be conducted May 7, 2000, from 1:00 to 5:00 p.m. in
conjunction with the PHYSOR 2000 Topical Meeting. The focus of the workshop will
be on new features and capabilities that are under development, especially with
respect to user interfaces and model visualization. Introduction and Overview A half-day workshop on recent advances in LANL's Monte Carlo N-Particle Transport
Code (MCNP) will be conducted May 11, 2000 from 1:30 to 5:30 p.m., in conjunction
with the PHYSOR 2000 Topical Meeting. The focus of the workshop will be on new
features and capabilities in the newly released version 4C. A half-day workshop on recent advances, new features and capabilities of the Penn
State PENTRAN multidimentional discrete ordinates program will be conducted on
Friday May 12, 2000, 8:00-12:00 in conjunction with the PHYSOR 2000 Topical
Meeting. A half-day workshop on major issues for automating variance reduction for Monte
Carlo shielding applications will be conducted on Friday May 12, 2000, 1-5 pm in
conjunction with the PHYSOR 2000 Topical Meeting. This course is aimed at the HP, medical physicist, and rad engineer with no prior
experience with Monte Carlo techniques. The focus is almost entirely on the
application of MCNP to solve a variety of practical problems in radiation shielding and
dosimetry. The intent is to "jump start" the student toward using MCNP productively.
Extensive interactive practice sessions are conducted on a personal computer. Topics
will include overview of the MCNP code and the Monte Carlo method, basic concepts,
input file preparation, geometry, source definition, standard MCNP tallies,
interpretation of the output file, exposure and dose rate calculations, radiation
shielding, photon skyshine, detector simulation and dosimetry. The course fee includes a complete MCNP code package, distributed directly from the
Radiation Safety Information Computational Center (RSICC). Students will also be
provided with a comprehensive class manual and a diskette containing all of the
practice problems. This course has been granted 32 Continuing Education Credits by
the AAHP. The course is offered by the Health Physics Measurements Group at the
Los Alamos National Laboratory and is co-sponsored by RSICC. Registration is available online at http://drambuie.lanl.gov/~esh4/mcnp.htm; however,
to guarantee a space payment must be received prior to the registration deadline.
Make checks payable to the University of California (checks must be in U.S. dollars on
a U.S. bank) and mail together with name, address, and phone number to the address
above. The course is offered by Group ESH-4, Health Physics Measurements, Mail
Stop G761, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, NM 87545 USA and is
co-sponsored by RSICC. Inquiries regarding registration and class space availability should be made to David
Seagraves, 505-667-4959, fax: 505-665-6071, e-mail: dseagraves@lanl.gov. Technical
questions may also be directed to Dick Olsher, 505-667-3364, e-mail: dick@lanl.gov. Upcoming 2000 dates for the MCNP and Visual Editor Training Course are: October 9-12 in Richland, Washington. Cost $1400 The source code package can be obtained directly from RSICC. The class will combine teaching on MCNP physics, along with instructions on how to
use the visual editor. Computer demonstrations and exercises will focus on creating
and interrogating input files with the visual editor. Demonstrations of advanced
visualization work using MCNP will also be made. The class will be taught on Pentium
computers running the Linux operating system. Attendees are encouraged to bring
their own input files for viewing and modifying in the visual editor. It is recommended
that you have experience with MCNP before taking this class. For additional
information contact Randy Schwarz, MS K8-34, P. O. Box 999, Richland, WA 99352
(509-372-4042, fax 509-372-6421, email randy.schwarz@pnl.gov, url
http://www.pnl.gov/eshs/software/ved.html). The following is the 2000 schedule for Monte Carlo N-Particle Transport Code
workshops.
Advanced classes are for people with MCNP experience who want to extend their
knowledge and understanding. Most areas of MCNP operation will be discussed in
detail, with emphasis on advanced geometry, advanced variance reduction
techniques, perturbation enhancement & cumulative tallies. Time will be available to
discuss approaches to specific problems of interest to students. NOTE: While MCNP supports a number of platforms, class computers are usually UNIX
machines. Experience with UNIX will be helpful to the student but is not essential. Year 2000 classes will showcase the latest release of MCNP, Version 4C. Major new
features that will be discussed include: All classes provide interactive computer learning. Time will be available to discuss
individual questions and problems with MCNP experts. To Register for the LANL
classes via the Internet, go to http://www.solutionsbyhqc.com/mcnpform.html or email
Bill Hamilton at bill@solutionsbyhqc.com. For registration information on the
European classes, contact Enrico Sartori, OECD/NEA, Sartori@nea.fr. Contact Judi
Briesmeister, email jfb@lanl.gov, for the course in Japan. The Department of Nuclear Engineering at the University of Tennessee-Knoxville is
offering two short courses for radiation transport specialists during Tennessee
Industries Week (TIW-35), August 14-18, 2000. Monte Carlo Analysis is often the method of choice to solve complex problems in
criticality and radiation shield design. The transport analyst must often choose
between Monte Carlo and deterministic methods like discrete ordinates; or the nature
of the design problem may dictate that he perform a coupled (Monte Carlo/discrete
ordinates) calculation. Therefore, to use Monte Carlo and other transport methods
effectively, the analyst must understand the theoretical and computational
fundamentals. Rather than use an existing program, it is sometimes advantageous to
create a new special-purpose Monte Carlo program. The procedures that are involved
in preparing a user-written Monte Carlo program will be described in terms of the
classical and conceptually simple straight-ahead, one-speed, slab transmission
problem. Many advanced topics will be included that will permit optimum use of existing
computer codes such as MCNP. Special attention will be given to the understanding of
the adjoint calculation. Advantages and disadvantages of the adjoint mode versus the
forward mode of analysis will be described. The full range of variance reduction
techniques will be studied for both forward and adjoint calculations. The Monte Carlo Method offers the expectation that the true solution to the problem as
modeled can be achieved. However, this may lead to a false sense of credibility, in
particular when calculations are performed by relatively inexperienced users (the
majority of people who use the Monte Carlo method do so only occasionally). Monte
Carlo calculations are subject to major errors and/or misinterpretations because
currently used statistical measures may be insufficient. Other methods for statistically
characterizing Monte Carlo methods will be described. The relationship of the Monte Carlo method to the other transport methods such as
discrete ordinates will be described, including comparisons of computational
advantages and disadvantages. The MCNP computer code will be described as
required to illustrate the general features of large Monte Carlo computer programs. Nuclear Criticality Safety Engineers, scientists, and technical managers who wish to
increase their knowledge and understanding of nuclear criticality safety will be
interested in this intensive one-week short course. The topics covered in the course
are based primarily on the experience of the six instructors which totals over 130
years of nuclear criticality safety related experience. Such a wealth of experience
needs to be shared with the criticality safety community including both new
professionals in the field as well as experienced professionals. The course topics include illustrative applications using the SCALE system developed
at Oak Ridge National Laboratory with emphasis on the Monte Carlo code KENO Va,
standards, regulations, review of accidents, hand calculation methods, subcritical
limits, code validation techniques, emergency response, process upsets and recovery
actions, and transient excursion modeling. The registration fee is $1195 per person for each course. The deadline for registration
in these courses is August 1, 2000. For additional information contact Lydia Salmon,
Dept. of Nuclear Engineering, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996 (phone
865-974-2525; email lutne@utk.edu). If you have access to the internet, you may also
register via the website at http://www.engr.utk.edu/dept/nuclear/TIW.html. The Fourth International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications (SNA
2000) September 4-7, 2000, Toranomon-Pastoral, Tokyo, Japan, sponsored by Japan Atomic
Energy Research Institute, cosponsored by OECD/Nuclear Energy Agency, Atomic
Energy Society of Japan, Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute. The objective of this conference is to present the newest research results in numerical
simulations in a wide variety of scientific and engineering fields, and to promote and
encourage the introduction of supercomputing technologies to numerical simulations.
Contributions generally focus on large scale numerical simulations in application
fields and supercomputing technologies. Papers on computational science and
engineering simulations, whether they are small or large scale, are welcome. Authors interested in contributing to the SNA 2000 are invited to submit manuscripts
that report new technologies and practical experience related to numerical simulations
in application fields and high performance computing and communication. Topics of
interest include but are not restricted to the following: Numerical Simulations in Application Fields High Performance Computing and Communication Hideo Kaburaki The International Conference on Advanced Monte Carlo for Radiation Physics, Particle
Transport Simulation and Applications (MC2000) will be held October 23-26, 2000, in
Lisbon, Portugal. At the International Conference, "Monte Carlo 2000 - Advanced
Monte Carlo for Radiation Physics, Particle Transport Simulation and Applications," all
sessions will be dedicated to Monte Carlo issues. This Conference has been organized
around three main categories of Monte Carlo simulations: Radiation Physics, Particle
Transport Simulation and Applications involving electron-photon, neutron-gamma and
hadronic codes. The following issues will be addressed: The deadline for abstract submission is March 31, 2000. Inquiries regarding the
conference can be addressed to: Instituto Tecnológico e Nuclear, MC2000 Conference
Secretariat, Estrada Nacional 10, P-2686-953 Sacavem, Portugal (phone: +351-21-994
60 00 ext. 6154, fax +351-21-994 10 39, email mc2000@itn1.itn.pt, or Dr. Pedro Vaz,
Technical and Scientific Program Co-ordinator at email vaz@nea.fr, url
http://www.itn.pt/Meetings/MC2000/). Your attention is directed to the following events of interest. May 2000 PHYSOR 2000, May 7-11, 2000, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, sponsored by the Reactor
Physics Section of the American Nuclear Society and the ANS Pittsburgh Section.
Contact: Dr. Tom Congedo (phone 412-256-1084, fax 412-256-2444, email
congedtv@westinghouse.com, url http://ans-pgh.commerce.wec.com/rp2000.htm). Workshop on Recent Advances Doors, ½-day May 7, 2000, in conjunction with
PHYSOR 2000, Pittsburgh. Contact: Yousry Azmy, yya@ornl.gov, url
http://nas.cped.ornl.gov/doors_ws00.html. You can register for the workshop by
making the appropriate selection on the general PHYSOR 2000 registration form. Early
registration is strongly encouraged due to limited space. New Capabilities in MCNP4C, ½-day May 11, 2000, in conjunction with PHYSOR 2000,
Pittsburgh. Contact: John S. Hendricks (mcnp@lanl.gov). Transport Processes in Applied Physics and Risk Analysis, A Tribute to Jacques
Devooght, May 12, 2000, Brussels. Contact: Mrs. Nicole Detienne, Service de Chimie
Organique, Faculté des Sciences Appliquées, Université Libre de Bruxelles, Bruxelles,
Belgium (phone 32-02-6502048, fax 32-02-6503606, email ndetienn@ulb.ac.be, url
http://mnsgi.ulb.ac.be/pub/pel/may12.html). MCNP Introductory Class, 23-26 May, 2000, Los Alamos National Laboratory, New
Mexico. To register for the LANL classes via the Internet, go to
http://www.solutionsbyhqc.com/mcnpform.html or email Bill Hamilton at
bill@solutionsbyhqc.com. June 2000 International Workshop on Neutron Field Spectrometry in Science, Technology and
Radiation Protection, June 5-8, 2000, Pisa, Italy. Contact Horst Klein, PTB, dep. 6.4
`Neutron Metrology', Bundesallee 100, D-38116 Braunschweig, Germany (phone
49-531-592-6400, fax 49-531-592-7205, email horst.klein@ptb.de). 8th International Symposium on Radiation Physics (ISRP-8), June 5-9, 2000, Prague,
the Czech Republic. Contact: Professor Ladislav Musílek, Czech Technical University
in Prague, Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering, Bøehová 7, 115 19
Praha 1, Czech Republic (fax +4202 2320861, email musilek@br.fjfi.cvut.cz). 7th Workshop on Methodologies for Particle Transport Simulation of Nuclear Systems
(Design, Dosimetry and Shielding), June 26-30, 2000, Penn State University, University
Park, Pennsylvania. Contact: haghigha@gracie.psu.edu, or iaw@psu.edu or from the
website at http://gracie.psu.edu/wshop02/wshop02.html. July 2000 Plutonium Futures--The Science, July 10-13, 2000, Santa Fe, New Mexico. Contact:
Plutonium Futures--The Science, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Nuclear Materials
Technology Division, P.O. Box 1663, MS E500, Los Alamos, NM, USA 87545 (phone
505-665-5981, fax 505-667-7966, email Puconf2000@lanl.gov). August 2000 Eighth International Conference on Electronic Spectroscopy and Structure (ICESS),
Campus of the University of California, Berkeley, Aug. 8-12, 2000. Contact:
icess@lbl.gov (url: http://www-als.lbl.gov/icess/). Monte Carlo Analysis, Aug. 14-18, 2000, Knoxville, Tennessee, a short course by the
University of Tennessee. Contact: Lydia Salmon, Dept. of Nuclear Engineering,
University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996 (phone 865-974-2525; email
lutne@utk.edu, http://www.engr.utk.edu/dept/nuclear/TIW.html. Nuclear Criticality Safety, Aug. 14-18, 2000, Knoxville, Tennessee, a short course by
the University of Tennessee. Contact: Lydia Salmon, Dept. of Nuclear Engineering,
University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996 (phone 865-974-2525; email
lutne@utk.edu, http://www.engr.utk.edu/dept/nuclear/TIW.html ). September 2000 4th International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications (SNA 2000),
Sept. 4-7, 2000, Toranomon-Pastoral, Tokyo, Japan, sponsored by Japan Atomic
Energy Research Institute, cosponsored by OECD/Nuclear Energy Agency, Atomic
Energy Society of Japan, Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute. Contact: Hideo
Kaburaki, Center for Promotion of Computational Science and Engineering, Japan
Atomic Energy Research Institute (phone +81-3-5723-2513, fax +81-3-5723-2537,
e-mail: sna2000@koma.jaeri.go.jp, http://ciscper.tokai.jaeri.go.jp/sna2k/ ) Radiation Protection for our National Priorities: Medicine, the Environment, and the
Legacy, Sept. 17-21, 2000, Spokane, Washington. Contact: Harvey Goldberg,
ANS-EWS, P.O.Box 941, Richland, WA 99352 (email finfrock@ambinet.com). SPECTRUM 2000, Chattanooga, Tennessee, Sept. 24-28, 2000. Contact: SPECTRUM
2000, University of Tennessee, Department of Nuclear Engineering, Knoxville, TN
37996-2300 (phone 865-974-5048, fax 419-828-4819, email
spectrum2000@engr.utk.edu, url http://www.engr.utk.edu/spectrum/). ICENES 2000, The 10th International Conference on Emerging Nuclear Energy
Systems, Sept. 25-28, 2000, Petten, The Netherlands. Contact: Mrs. M. Hofman,
Meeting Secretariat, NRG, P.O. Box 25, 1755 ZG Petten, The Netherlands (phone
+31-224-56-4193, fax +31-224-56-3490, email hofman@nrg-nl.com, url
http://www.nrg-nl.com/congres/icenes/). October 2000 YUNSC 2000, Oct 2-5, 2000, Belgrade, Yugoslavia. Contact: Radojko Pavlovi, YUNSC
2000 Conference Secretary, The VINCA Institute of Nuclear Sciences, P.O.B. 522, 11001
Belgrade, Yugoslavia (phone + 381-11-453-867, fax + 381-11-455-943, email
yuns@rt270.vin.bg.ac.yu). MCNP and Visual Editor Training Course, Oct. 9-12, 2000, Richland, Washington.
Contact: Randy Schwarz, MS K8-34, P. O. Box 999, Richland, WA 99352 (509-372-4042,
fax 509-372-6421, email randy.schwarz@pnl.gov, url
http://www.pnl.gov/eshs/software/ved.html). 2000 American Nuclear Society 14th Topical Meeting on the Technology of Fusion
Energy, Oct. 15-19, 2000, Park City, Utah. Contact: url
http://www.ambinet.com/ans/rps2000.htm. 4th International Workshop on Dosimetry for Radiation Processing, Oct. 22-27, 2000,
San Diego, California. Contact: Dr. Harry Farrar IV, ASTM Committee E-10, 18 Flintlock
Lane, Bell Canyon, CA 91307-1127 (phone 818-340-1227, fax 818-340-2132, email
hfarrar4@aol.com). International Conference on Advanced Monte Carlo for Radiation Physics, Particle
Transport Simulation and Applications (MC2000), October 23-26, 2000, Lisbon,
Portugal. Contact: Intituto Tecnológico e Nuclear, MC2000 Conference Secretariat,
Estrada Nacional 10, P-2686-953 Sacavem, Portugal (phone: +351-21-994 60 00 ext.
6154, fax +351-21-994 10 39, email mc2000@itn1.itn.pt, or Dr. Pedro Vaz, Technical and
Scientific Program Co-ordinator at email vaz@nea.fr, url http://lipulsi.lip.pt/mc2000/). November 2000 5th Radiation Physics Conference--Atomic Energy, Radiation Protection, Challenges
and Strategies, Nov. 5-9, 2000, Cairo, Egypt. Contact: Prof. Mohammad A. Gomaa,
Atomic Energy Authority, 3 Ahmad Al-Zomor St., Alzohour District, Nasr City, Children
Village Post Office, Postal Code 11787, Cairo, Egypt (fax 00202-287603, email
ruatom@rusys.EG.net).
What's New With DOORS
PRELIMINARY PROGRAM 
The workshop will be presented by research staff from the ORNL Nuclear Analysis
and Shielding Section. Questions regarding the workshop should be directed to
Yousry Azmy (yya@ornl.gov). You can register for the workshop by making the
appropriate selection on the general PHYSOR 2000 registration form. Early
registration is strongly encouraged due to limited space. The latest version of
DOORS can be obtained as Code Package CCC-650 from the Radiation Safety
Information Computational Center, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, P.O. Box 2008,
Oak Ridge, TN 37831-6362 (865-574-6176). The latest user information on DOORS is
available in the DOORS Electronic Notebook.
New Capabilities in MCNP4C
PRELIMINARY PROGRAM
Questions regarding the workshop should be directed to John S. Hendricks
(mcnp@lanl.gov). For more information about MCNP and internationally offered
courses, see the MCNP Homepage: http://www-xdiv.lanl.gov/XCI/PROJECTS/MCNP
Register for the workshop by making the appropriate selection on the PHYSOR 2000
Registration Form. Early registration is strongly encouraged due to limited space.
PENTRAN 3-D Parallel Sn (PSU)
PROGRAM PENTRAN - 3D Parallel Sn Code System
INTRODUCTION
- Boltzmann equation
- Discrete Ordinates method
Sn MAJOR ISSUES
- Numerics (quadratures, differencing, ...)
- Mesh generation
- Cross section preparation
- Input preparation
- Sn codes
INTRODUCTION TO PENTRAN CODE
- Introduction and features
- Verification and validation
- Parallel performance on different platforms
- A sample PENTRAN input file
PENTRAN CODE SYSTEM
- PENMSH: 3-D mesh generator
- PENINP: Automated input preparation
- PENTRAN: 3-D parallel Sn code
- PENDATA/PENPRL: Post-processing
PENTRAN COMPUTER EXERCISES
- Demonstration
- Hands-on exercisesQuestions regarding the workshop should be directed to Prof. Ali. Haghighat
(haghighat@psu.edu). The workshop homepage is
http://www.hsact.com/physor02.htm.
Automated Variance Reduction with A3MCNP for Shielding Problems
(PSU)
PROGRAM INTRODUCTION
- Monte Carlo Method
- Tallies
- Precision, Quality of Results (Sigma, R, FOM)
MAJOR ISSUES
- Importance of Variance Reduction
- Shielding Example
CADIS METHODOLOGY
- Importance Function
- Source and Transport Biasing
- Consistent Adjoint-Driven Importance Sampling
A3MCNP
- Implementation of CADIS in MCNP
- Automatic Sn Input Preparation (mesh, cross sections)
- A3MCNP Input and Procedures
BENCHMARKING OF A3MCNP
- Verification and Validation
- Performance for Shielding Problems
A3MCNP COMPUTER EXERCISES
- Demonstration
- Hands-on ExercisesQuestions regarding the workshop should be directed to Prof. Ali. Haghighat
(haghighat@psu.edu). The workshop homepage is
http://www.hsact.com/physor02.htm. Practical MCNP for the Health /Medical Physicist & Rad
Engineer
MCNP and Visual Editor Training Course
MCNP Workshops for the Year 2000
Year 2000 Schedule: 23-26 May
Introductory Class
USA, Los Alamos National Laboratory 3-7 July
Introductory Class
University of Stuttgart, Germany 12-15 September
Introductory Class
Richland, Washington 11-15 September
MCNP Topics
Tokyo, Japan
Reactor Analysis and Criticality Safety Short Courses
SNA 2000
Center for Promotion of Computational Science and Engineering
Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute
Tel. +81-3-5723-2513
Fax. +81-3-5723-2537
e-mail: sna2000@koma.jaeri.go.jp
http://ciscper.tokai.jaeri.go.jp/sna2k/ MC2000
Calendar