 |
Oak Ridge National Laboratory Post Office Box 2008 Oak Ridge, Tennessee 37831-6362 Managed by UT-Battelle, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy under contract DE-AC05-00OR22725 Phone No. 865-574-6176 FAX 865-574-6182 Internet: PDC@ORNL.GOV WWW: http://www-rsicc.ornl.gov/rsic.html |
| No. 423 | April-May 2000 |
| Every man has a property in his own person; this nobody has a right to but himself. -- Locke | |
- RSICC Documentation in PDF Format
- Listserver Now Available for NJOY Users
- NRC Codes Made Available
- CHANGES TO THE COMPUTER CODE COLLECTION
- CHANGES TO THE DATA LIBRARY COLLECTION
- Obituaries
- ICRU Publishes Nuclear Data Report with Data CD
- NCRP Announces Results of Membership Elections
- CONFERENCES, COURSES, SYMPOSIA
- Practical MCNP for the Health /Medical Physicist & Rad Engineer
- MCNP and Visual Editor Training Course
- MCNP Workshops for the Year 2000
- Calendar
- MARCH ACCESSION OF LITERATURE
RSICC Documentation in PDF Format
RSICC will begin distributing documentation in electronic Portable Document Format (PDF) for viewing with the Adobe Acrobat Reader. Electronic documentation has been available on our web site for quite some time, but we have continued to distribute hard copy reports as well. For new packages distributed on CD, the electronic documentation will be included. Hardcopies will no longer be distributed. Large documents will be indexed. Users may print selected pages or the entire document. To view the files electronically, Acrobat Reader must be installed on your computer. It may be downloaded from:
http://www.adobe.com/acrobat/readstep.html
Listserver Now Available for NJOY Users
A new NJOY Listserver to facilitate exchange of information on NJOY has been implemented. Bob MacFarlane of Los Alamos National Laboratory and Enrico Sartori of the Nuclear Energy Agency Data Bank moderate the list to make sure that messages from commercial advertising are filtered out and that only relevant information for the scope of the NJOY discussion forum is circulated. The historical archive of the NJOY User Group Notes produced in the previous years will be posted soon. More information on the scope of the NJOY Listserver and the rules or "netiquette" for circulating messages can be found at http://www.nea.fr/lists/njoy.html.
NRC Codes Made Available
Several U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) software packages which were transferred from the Energy Science and Technology Software Center, Oak Ridge, Tennessee to RSICC were incorporated into the RSICC computer code collection. Please browse the computer code abstracts available at RSICC's www site for more information on these packages.
PSR-445/VISA2
PSR-466/MAEROS
PSR-476/SPIRT
PSR-478/GRFPAK
CHANGES TO THE COMPUTER CODE COLLECTION
Four new code systems were added to the computer code collection during the month. Two additions resulted from foreign contributions.
 The UK Department of the Environment (DOE), London, England, through the NEA
DB contributed this code system which provides an estimate of the subsequent
radiological risk to man by simulating the ground water mediated movement of
radionuclides from underground facilities for the disposal of low and intermediate
level wastes to the accessible environment. The simulated timescales are usually
within the range 103 to 107 years. SYVAC is capable of modelling both shallow
disposal facilities and deep disposal facilities. It includes both vault and geosphere
submodels.
The UK Department of the Environment (DOE), London, England, through the NEA
DB contributed this code system which provides an estimate of the subsequent
radiological risk to man by simulating the ground water mediated movement of
radionuclides from underground facilities for the disposal of low and intermediate
level wastes to the accessible environment. The simulated timescales are usually
within the range 103 to 107 years. SYVAC is capable of modelling both shallow
disposal facilities and deep disposal facilities. It includes both vault and geosphere
submodels.
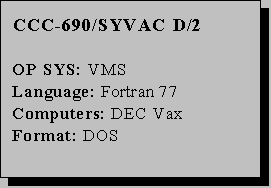
NEA DB executed the included test cases on a Vax 8810 computer under VMS version 4.3. SYVAC uses the Vax standard mathematical library but also requires the NAG (Numerical Algorithms Group) library or an equivalent for certain numerical routines not provided in standard Fortran libraries. The package includes the Fortran source, command files, test cases and electronic documentation (PDF) in DOS self-extracting, compressed files written on a CD. References: DOE/RW/89.084, DOE/RW/89.085, DOE/RW/89.086 (1988). Fortran 77; DEC Vax (C00690D0VAX00).
 Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico, contributed a new
version of this Monte Carlo N-particle transport code system. MCNP is a
general-purpose, continuous-energy, generalized geometry, time-dependent, coupled
neutron-photon-electron Monte Carlo transport code system. MCNP4C is the first
major release of MCNP since version 4B (February 4, 1997). The major new features
include:
Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico, contributed a new
version of this Monte Carlo N-particle transport code system. MCNP is a
general-purpose, continuous-energy, generalized geometry, time-dependent, coupled
neutron-photon-electron Monte Carlo transport code system. MCNP4C is the first
major release of MCNP since version 4B (February 4, 1997). The major new features
include:
* Unresolved resonance range probability tables;
* Perturbation enhancements;
* Superimposed mesh weight window generator;
* Alpha eigenvalues;
* Macrobodies;
* ENDF/B-VI improvements;
* PC Enhancements;
* Electron Physics enhancements;
* Parallelization enhancements;
* Delayed neutrons.
MCNP is operable on Cray computers under UNICOS, workstations under Unix or PCs under Linux, Windows NT/9x PCs, and Vax computers under VMS. Compilation requires both Fortran77 and ANSI C standard compilers. The source can be compiled with g77 on PCs running Red Hat Linux. Executables are included only for PCs running Windows; all other systems require a Fortran compiler. The PC executables were created in a DOS window of Windows 98 with Digital Visual Fortran Professional Edition 6.0A Fortran 90 compiler on a Pentium II. RSICC tested this release on several Unix workstations (IBM RS/6000, Sun, HP, DEC, and SGI); on a Pentium III running Red Hat Linux Version 6.1; on a Pentium II in a DOS window of Windows 98 with Digital Visual Fortran Professional Edition 6.0A Fortran 90 compiler with QuickWin plots; and on a Pentium II with Lahey/Fujitsu Fortran 95 Version 5.50 compiler with Winteracter Starter Kit.
The electronic documentation, source codes, test problems, executables, and installation scripts are distributed on CD-ROM and can be read under either Windows or UNIX operating systems. As a convenience to users, the DLC-200/MCNPDATA library is included on the distribution media. The cross sections are in ASCII mode in the Unix file and in binary mode for PC Windows users. References: Readme.txt (April 2000) and LA-13709-M (April 2000). Fortran 77 or 90 and C; Unix workstations, Intel-based Pentium PC, Cray, and Vax. (C00700ALLCP00).
 Gesellschaft f. Reaktorsicherheit (GRS) mbH, Garching, West Germany, through the
NEA DB contributed this code system based on a non-linear theoretical model
describing the steady-state and transient behavior of a vertical natural-circulation
U-tube steam generator together with its main steam system. The steam generator
consists of a heat exchange section, a top plenum, a down-comer region and a main
steam system (with a sequence of relief and/or safety valves, isolation, bypass,
turbine-trip and turbine-control valves and a steam turbine). The theoretical model
consists of a set of analytical state and nonlinear ordinary first-order differential
equations.
Gesellschaft f. Reaktorsicherheit (GRS) mbH, Garching, West Germany, through the
NEA DB contributed this code system based on a non-linear theoretical model
describing the steady-state and transient behavior of a vertical natural-circulation
U-tube steam generator together with its main steam system. The steam generator
consists of a heat exchange section, a top plenum, a down-comer region and a main
steam system (with a sequence of relief and/or safety valves, isolation, bypass,
turbine-trip and turbine-control valves and a steam turbine). The theoretical model
consists of a set of analytical state and nonlinear ordinary first-order differential
equations.
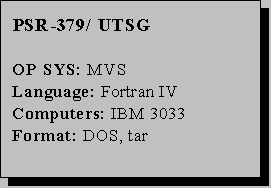
UTSG was tested at the NEA Data Bank on an IBM 3033 under MVS. With minor source changes, it was executed on an IBM RS/6000 at RSICC. A Fortran compiler is required. The package is transmitted on a DS/HD diskette which includes the Fortran source and test case transmitted in both DOS and Unix compressed formats. Reference: GRS-A-426 (March 1980). IBM 3033; Fortran IV (P00379I303300).
 Through the NEA Data Bank, ORNL contributed this code system for analysis of
steam turbine cycles supplied by light-water reactors. ORCENT-2 performs heat and
mass balance calculations at valves-wide-open design conditions, maximum
guaranteed rating conditions, and an approximation of part-load conditions for steam
turbine cycles supplied with throttle steam, characteristic of contemporary light-water
reactors. The program handles both condensing and back-pressure turbine exhaust
arrangements. Turbine performance calculations are based on the General Electric
Company method for 1800-rpm large steam turbine-generators operating with
light-water-cooled nuclear reactors. Output includes all information normally shown
on a turbine-cycle heat balance diagram.
Through the NEA Data Bank, ORNL contributed this code system for analysis of
steam turbine cycles supplied by light-water reactors. ORCENT-2 performs heat and
mass balance calculations at valves-wide-open design conditions, maximum
guaranteed rating conditions, and an approximation of part-load conditions for steam
turbine cycles supplied with throttle steam, characteristic of contemporary light-water
reactors. The program handles both condensing and back-pressure turbine exhaust
arrangements. Turbine performance calculations are based on the General Electric
Company method for 1800-rpm large steam turbine-generators operating with
light-water-cooled nuclear reactors. Output includes all information normally shown
on a turbine-cycle heat balance diagram.
ORCENT-2 was developed on IBM 360/370 computers and requires a Fortran IV compiler. It was tested at the NEA Data Bank on an IBM 3033 running OS/VS2 with the H-extended compiler. The code was not tested when it was transmitted to RSICC in February 2000. The package is transmitted on a DS/HD diskette which includes the source and sample problem in compressed DOS and Unix compressed formats. Reference: ORNL/TM-6525 (February 1979); Fortran IV; IBM 360/370 (P00474I303300).
CHANGES TO THE DATA LIBRARY COLLECTION
One addition was made to the data library collection during the month.
 Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico, contributed these
cross-section libraries for use with Version 4C and later of the MCNP transport code.
These data provide a comprehensive set of cross sections for a wide range of radiation
transport applications using the Monte Carlo code package CCC-700/MCNP4C.
Documentation is available at:
Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico, contributed these
cross-section libraries for use with Version 4C and later of the MCNP transport code.
These data provide a comprehensive set of cross sections for a wide range of radiation
transport applications using the Monte Carlo code package CCC-700/MCNP4C.
Documentation is available at:
http://www-xdiv.lanl.gov/XCI/PROJECTS/DATA/nuclear/avdoc.htm.
A wide variety of continuous-energy, discrete, multigroup, thermal and dosimetry neutron data libraries are available in this release. The continuous-energy neutron data libraries available include: ENDF60, RMCCS, RMCCSA, ENDF5U, ENDF5P, NEWXS, ENDF5MT, MISC5XS, ENDL85, KIDMAN, 100XS, URES, ENDF6DN, ENDF62MT, and ENDL92. The discrete neutron data libraries include: NEWXSD, DRMCCS, and DRE5. The multigroup neutron data library is MGXSNP, and the thermal S(alpha, beta) libraries are TMCCS and THERXS. The neutron dosimetry libraries are 531DOS, 532DOS, and LLLDOS. The photon transport libraries are MCPLIB and MCPLIB02, and the electron libraries are EL and EL03. The photon and electron data libraries contain data for elements having Z<95.
The data library ENDF5MT contains data previously available in the library EPRIXS, along with the U600K data library. The data library MISC5XS contains corrected data for ENDF/B-V based Zr as described below, and the libraries previously known as IRNAT, MISCXS, ARKRC, TM169, GDT2GP, and T2DDC. The ENDF/B-V Zr data has been corrected for five ZAID's from the libraries RMCCS, DRMCCS, ENDF5P, DRE5, and EPRIXS. These five data libraries (URES, ENDF6DN, ENDF62MT, ENDL92, and EL03) are newly released. Please consult the README file and the more detailed documentation provided for descriptions of these libraries.
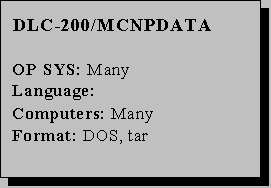
All data libraries in the Unix tar file are in ASCII format and can be used with MCNP4C on all computer platforms supported by the code. Files distributed in compressed mode on the distribution CD can be read under either Windows or Unix. A self-extracting compressed file for Windows users contains both the MCNP4C code system with executables and cross-sections from MCNPDATA in binary format for PC users. Expanding the code system (50 MB) and binary cross section libraries (360MB) under Windows requires ~410 MB of hard disk space. Unix users need more because the ASCII cross sections require 880 MB of hard disk space.
References: The following documents are distributed in electronic (PDF) form with the package: Revised Table G.2 for Appendix G of the MCNP4C manual, README (April 2000), LA-12891 (1994), X-6:HGH-93-77 (revised 1996), XTM:95-259 and LA-UR-96- 24 (1995), X-6:RCL-87-225 (1987), XCI-RN(U)98-041, LA-UR-98-5718, (December 1998), XTM:96-153 (April 1996), and XCI:CJW-99-25 (April 1999) (D00200ALLCP00).
Obituaries
Much of the following information about Dr. Zinn, Maj. Gen. Nichols, and Dr. Eklund came from ANS Nuclear News (April 2000).
Dr. Walter H. Zinn , 93, died at a hospital in Clearwater, Florida, February 14, 2000. He was born December 10, 1906, in Kitchner, Ontario, Canada. He received BA and MA Degrees from Queens University, Kingston, Ontario, and a Ph.D in Physics from Columbia University, New York City. Dr. Zinn was internationally known for his contributions in physics and reactor engineering. In the mid 30s he collaborated with Leo Szilard on an experiment crucial to proving the feasibility of the fission chain reaction, the measurement of the number of prompt neutrons emitted per uranium fission. He was a leader in Enrico Fermi's wartime team which constructed the world's first nuclear reactor. He headed one of the teams in charge of the construction of the CP-1 reactor and was subsequently responsible for the design and construction of the world's first heavy-water moderated reactor--CP-3--which was placed in operation in 1944.
Dr. Zinn was named the first director of the Argonne National Laboratory in 1946 and served in that capacity for ten years. He made significant contributions to the design and development of a number of nuclear reactors, including the Experimental Breeder Reactor No. 1 (nicknamed ZIP for Zinn's Infernal Pile), which produced the first electricity from nuclear energy in 1951 and first demonstrated the breeding of nuclear fuel; the Submarine Thermal Reactor, the prototype for the power plant of Nautilus, the first nuclear-powered submarine; the Savannah River Reactors for plutonium production; the Argonne Heavy Water Research Reactor, or CP-5; the Borax Nuclear Power Plant, the first boiling water reactor; the Experimental Boiling Water Reactor; and the Experimental Breeder Reactor No. 2.
In 1956 he founded the General Nuclear Engineering Corporation and served as president of that company until it merged with Combustion Engineering, Inc. (now ABB). He then served as vice president of the Nuclear Division and on the Board of Directors and Consultant until he retired in 1970. He served on the President's Science Advisory Committee for Presidents Eisenhower, Kennedy, Johnson and Nixon. He was a co-recipient of the Ford Foundation Atoms-for-Peace Award in 1960. In 1969 he received the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission's Enrico Fermi Award "For his pioneering work in atomic energy, including the world's first reactors and the fast breeder reactor, and for his distinguished record of leadership and contributions to the development of atomic reactors for research, production, and electric power."
He was a charter member of the American Nuclear Society and served as its president in 1955-56. The Power Division of the American Nuclear Society created the Walter H. Zinn Award in 1978, making him the first recipient.
Maj. Gen. Kenneth D. Nichols, 92, died February 21 in Bethesda, Maryland. Nichols helped establish early military and civilian nuclear policies. He worked on the Manhattan Project in 1942 and oversaw the construction of the Oak Ridge, Tennessee, and Hanford, Washington, projects. In 1953 he became general manager of the Atomic Energy Commission and promoted the construction of nuclear power plants.
In "My Work In Oak Ridge," the chapter he wrote for These Are Our Voices (January 1987, Childrens Museum of Oak Ridge; ISBN: 0960683240) he had this to say about the making of a community in which both scientists and "hillbillies" would live.
"The town of Oak Ridge itself required approximately $100 million for construction, or about one-tenth of the overall cost of the Clinton Engineer Works. More headaches for me, however, were generated per dollar spent in the construction and operation of the town than for any of the production plants. Handling personnel on a construction job was one thing, but being responsible for the men, women and children in a government-owned town of which the best that can be said for the form of government is that it was a benevolent dictatorship, was another matter ...
| "We had many diverse opinions about how to operate the town. Some wanted to run social experiments, such
as establishing a unified church. However, I felt that the more normal the town, the better; and that was the
policy finally established. ... Oak Ridge was a city without a past, and it was not designed to have much of a
future. ... The very fact, however, that Oak Ridge is a thriving town today shows that the foundations laid
were more lasting than we expected. ...
"After spending three exciting years of my life planning, constructing and living in Oak Ridge, I am pleased that this once temporary town has fixed its place, permanently, in the history and future of those other towns that make up Tennessee." |
He returned to Oak Ridge in 1998 for the Special Engineer Detachment reunion.
Sigvard Arne Eklund, 89, ANS Fellow and member since 1958, died January 30 in Vienna. During his career he served the Nobel Institute of Physics as an assistant then senior scientist. Eklund was a senior scientist at the Research Institute for National Defense in Stockholm. He was director of research at the Swedish Atomic Energy Company. He also served as deputy to the managing director of AB Atomenergi. He was Secretary General for the Second International United Nations Conference on the Peaceful Uses of Atomic Energy. In 1961 he became the second director general of the International Atomic Energy Agency and served in that capacity for 20 years. He was born in Kiruna, Sweden, in 1911.
ICRU Publishes Nuclear Data Report with Data CD
The International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (ICRU) announced the publication of ICRU Report 63, Nuclear Data for Neutron and Proton Radiotherapy and for Radiation Protection. Report 63 includes an extensive compilation of data on a compact disc. This publication is a comprehensive tabulation of nuclear data relevant for medical, industrial, research, and protection applications. Extensive microscopic cross-sections for neutron and proton interaction with elements important to dosimetry, radiation transport, and industrial applications are provided. For each application, the granularity of the data tabulations reflects the anticipated needs. For example, the data for tissue elements, H, C, N, and O, are very complete with a fine energy grid. In contrast, the data for iron and lead are designed for shielding calculations and radiation transport. Elastic and inelastic and total cross section data are extensive, but secondary charged particle producing reaction data are sparser. A coarser energy grid is used. Considerable data are supplied in the Report, but the accompanying CD-ROM contains very extensive compilations in an easily understood format, "ENDF-easy."
In addition to their obvious value in radiotherapy and radiation protection, these data are useful for many other applications and are essential for space exploration, long-range high-altitude air flights, and radiation protection near high-energy accelerators. Neutron-induced nuclear reaction cross sections and kerma coefficients are presented up to 150 MeV, and proton-induced cross sections are presented up to 250 MeV. Potential uses of these data include their implementation in radiation transport and treatment planning computer codes to optimize dose delivery to the treatment volume; studies of the impact of nuclear reactions on the relative biological effectiveness of neutron and proton therapy beams; determination of radiation shielding requirements; calculation of protection quantities (organ doses, effective dose) and operational quantities (dose equivalent); and use of kerma coefficients to determine absorbed dose for a given neutron energy distribution, and to convert the absorbed dose, measured with a dosimeter of a given material composition, to absorbed dose in tissue. The nuclear cross sections are evaluated using a combination of measured data and nuclear model calculations. The Report reviews measurements from which cross sections and kerma coefficients have been determined, but since there are only a limited number of experimental data sets for biologically-important target elements, theoretical predictions are needed to supplement these data. For this purpose, use is made of the GNASH nuclear model code, which applies theories for compound nucleus, preequilibrium, and direct reaction mechanisms. Optical model calculations determined total, total nonelastic and elastic scattering cross sections. Numerous benchmarks compare the model predictions with measured data to validate the calculations of energy- and angle-dependent emission spectra, as well as total, nonelastic, and elastic scattering cross sections. For hydrogen, an evaluation is described that uses both R-matrix and phase-shift scattering theories to represent neutron-proton reaction data. Kerma coefficients are derived from the evaluated neutron-induced cross sections and presented for individual elements as well as for ICRU muscle, A-150 tissue-equivalent plastic, and other compounds which are important for treatment planning and dosimetry.
Individuals and organizations already on the ICRU Publications Standing Order List will receive copies of the new report automatically and be invoiced for their order. Others may purchase copies of the new report for US $95 (payment may be made via Visa, Master Card, or American Express credit cards) or place their name on the Standing Order List by directing their order to: ICRU Publications, 7910 Woodmont Ave., Suite 800, Bethesda, MD 20814 (phone 301-657-2652, fax 301-907-8768, email icru@icru.org).
ICRU Press Release (April 14, 2000)
NCRP Announces Results of Membership Elections
The National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP) announced today the results of the regular membership elections which took place at its Thirty-Sixth Annual Meeting on April 6, 2000. Newly elected were: Benjamin Archer, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas; Eleanor Blakely, E.O. Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, California; John Dicello, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland; Stephen Feig, The Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, New York; Kenneth Foster, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia; Ritsuko Komaki, The University of Texas, M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston; Jay Lubin, National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, Maryland; C. Douglas Maynard, Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, North Carolina; Claire Mays, Institut Symlog, Paris, France.
CONFERENCES, COURSES, SYMPOSIA
RSICC attempts to keep its users/contributors advised of conferences, courses, and symposia in the field of radiation protection, transport, and shielding through this section of the newsletter. Should you be involved in the planning/organization of such events, feel free to send your announcements and calls for papers via email to finchsy@ornl.gov with "conferences" in the subject line. Please include the announcement in its native format as an attachment to the message. If the meeting is on a website, please include the url.
Every attempt is made to ensure that the links provided in the Conference and Calendar sections of this newsletter are correct and live. However, the very nature of the web creates the possibility that the links may become unavailable. In that case, please call or mail the contact provided.
Practical MCNP for the Health /Medical Physicist & Rad Engineer
DATES: 16-20 October 2000 (registration deadline 2 October 2000)
FEE: $1,700 per person (includes the MCNP code package)
PLACE: The Canyon School Complex, Los Alamos National Laboratory
This course is aimed at the HP, medical physicist, and rad engineer with no prior experience with Monte Carlo techniques. The focus is almost entirely on the application of MCNP to solve a variety of practical problems in radiation shielding and dosimetry. The intent is to "jump start" the student toward using MCNP productively. Extensive interactive practice sessions are conducted on a personal computer. Topics will include overview of the MCNP code and the Monte Carlo method, basic concepts, input file preparation, geometry, source definition, standard MCNP tallies, interpretation of the output file, exposure and dose rate calculations, radiation shielding, photon skyshine, detector simulation and dosimetry.
The course fee includes a complete MCNP code package, distributed directly from the Radiation Safety Information Computational Center (RSICC). Students will also be provided with a comprehensive class manual and a diskette containing all of the practice problems. This course has been granted 32 Continuing Education Credits by the AAHP. The course is offered by the Health Physics Measurements Group at the Los Alamos National Laboratory and is co-sponsored by RSICC.
Registration is available online at http://drambuie.lanl.gov/~esh4/mcnp.htm; however, to guarantee a space payment must be received prior to the registration deadline. Make checks payable to the University of California (checks must be in U.S. dollars on a U.S. bank) and mail together with name, address, and phone number to the address above. The course is offered by Group ESH-4, Health Physics Measurements, Mail Stop G761, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, NM 87545 USA.
Inquiries regarding registration and class space availability should be made to David Seagraves, 505-667-4959, fax: 505-665-6071, e-mail: dseagraves@lanl.gov. Technical questions may also be directed to Dick Olsher, 505-667-3364, e-mail: dick@lanl.gov.
MCNP and Visual Editor Training Course
Upcoming 2000 dates for the MCNP and Visual Editor Training Course are:
October 9-12 in Richland, Washington. Cost $1400
The source code package can be obtained directly from RSICC.
The class will combine teaching on MCNP physics, along with instructions on how to use the visual editor. Computer demonstrations and exercises will focus on creating and interrogating input files with the visual editor. Demonstrations of advanced visualization work using MCNP will also be made. The class will be taught on Pentium computers running the Linux operating system. Attendees are encouraged to bring their own input files for viewing and modifying in the visual editor. It is recommended that you have experience with MCNP before taking this class. For additional information contact Randy Schwarz, MS K8-34, P. O. Box 999, Richland, WA 99352 (509-372-4042, fax 509-372-6421, email randy.schwarz@pnl.gov, url http://www.pnl.gov/eshs/software/ved.html).
MCNP Workshops for the Year 2000
The following is the 2000 schedule for Monte Carlo N-Particle Transport Code Workshops.
| Year 2000 Schedule: | ||
| 3-7 July | Introductory Class | University of Stuttgart, Germany |
| 12-15 September | Introductory Class | Richland, Washington |
| 11-15 September | MCNP Topics | Tokyo, Japan |
Introductory classes are for people who have little or no experience with MCNP. The classes survey the features of MCNP so the beginning user will be exposed to the capabilities of the program and will have hands-on experience at running the code to solve rudimentary problems. Course topics include basic geometry, source definitions, output (tallies) specification and interpretation, advanced geometry (repeated structures specification), variance reduction techniques, statistical analysis, criticality, plotting of geometry, tallies, and particle tracks, and neutron/photon/electron physics.
Advanced classes are for people with MCNP experience who want to extend their knowledge and understanding. Most areas of MCNP operation will be discussed in detail, with emphasis on advanced geometry, advanced variance reduction techniques, perturbation enhancement & cumulative tallies. Time will be available to discuss approaches to specific problems of interest to students.
NOTE: While MCNP supports a number of platforms, class computers are usually Unix machines. Experience with Unix will be helpful to the student but is not essential.
Year 2000 classes will showcase the latest release of MCNP, Version 4C. Major new features that will be discussed include:
- Macrobodies
- Unresolved Resonance Treatment
- Perturbation Enhancement
- Alpha Eigenvalues
- Cumulative Tallies
All classes provide interactive computer learning. Time will be available to discuss individual questions and problems with MCNP experts. To Register for the LANL classes via the Internet, go to http://www.solutionsbyhqc.com/mcnpform.html or email Bill Hamilton at bill@solutionsbyhqc.com. For registration information on the European classes, contact Enrico Sartori, OECD/NEA, Sartori@nea.fr. Contact Judi Briesmeister, email jfb@lanl.gov, for the course in Japan.
Calendar
Your attention is directed to the following events of interest.
June 2000
International Workshop on Neutron Field Spectrometry in Science, Technology and Radiation Protection, June 5-8, 2000, Pisa, Italy. Contact: Horst Klein, PTB, dep. 6.4 `Neutron Metrology', Bundesallee 100, D-38116 Braunschweig, Germany (phone 49-531-592-6400, fax 49-531-592-7205, email horst.klein@ptb.de).
8th International Symposium on Radiation Physics (ISRP-8), June 5-9, 2000, Prague, the Czech Republic. Contact: Professor Ladislav Musílek, Czech Technical University in Prague, Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering, Bøehová 7, 115 19 Praha 1, Czech Republic (fax +4202 2320861, email musilek@br.fjfi.cvut.cz).
7th Workshop on Methodologies for Particle Transport Simulation of Nuclear Systems (Design, Dosimetry and Shielding), June 26-30, 2000, Penn State University, University Park, Pennsylvania. Contact: haghigha@gracie.psu.edu, or iaw@psu.edu or from the website at http://gracie.psu.edu/wshop02/wshop02.html.
July 2000
Plutonium Futures--The Science, July 10-13, 2000, Santa Fe, New Mexico. Contact: Plutonium Futures--The Science, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Nuclear Materials Technology Division, P.O. Box 1663, MS E500, Los Alamos, NM, USA 87545 (phone 505-665-5981, fax 505-667-7966, email Puconf2000@lanl.gov).
August 2000
Eighth International Conference on Electronic Spectroscopy and Structure (ICESS), Campus of the University of California, Berkeley, Aug. 8-12, 2000. Contact: icess@lbl.gov (url http://www-als.lbl.gov/icess/).
Monte Carlo Analysis, Aug. 14-18, 2000, Knoxville, Tennessee, a short course by the University of Tennessee. Contact: Lydia Salmon, Dept. of Nuclear Engineering, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996 (phone 865-974-2525, email lutne@utk.edu, url http://www.engr.utk.edu/dept/nuclear/ TIW.html).
Nuclear Criticality Safety, Aug. 14-18, 2000, Knoxville, Tennessee, a short course by the University of Tennessee. Contact: Lydia Salmon, Dept. of Nuclear Engineering, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996 (phone 865-974-2525, email lutne@utk.edu, url http://www.engr.utk.edu/dept/nuclear/TIW.html).
September 2000
4th International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications (SNA 2000), Sept. 4-7, 2000, Toranomon-Pastoral, Tokyo, Japan, sponsored by Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute, cosponsored by OECD/Nuclear Energy Agency, Atomic Energy Society of Japan, Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute. Contact: Hideo Kaburaki, Center for Promotion of Computational Science and Engineering, Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (phone +81-3-5723-2513, fax +81-3-5723-2537, e-mail: sna2000@koma.jaeri.go.jp, http://ciscper.tokai.jaeri.go.jp/sna2k/).
International Conference Nuclear Energy in Central Europe 2000, Sept. 11-14, 2000, Bled, Slovenia. Leon Cizelj, Institut "Joef Stefan", Ljubljana, Slovenija Odsek za reaktorsko tehniko / Reactor Engineering Division Jamova 39, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia (tel + 386 1 5885 215, fax + 386 51 561 23 35, url http://kastor.ijs.si/~bled2000)
Radiation Protection for Our National Priorities: Medicine, the Environment, and the Legacy, Sept. 17-21, 2000, Spokane, Washington. Contact: Harvey Goldberg, ANS-EWS, P.O.Box 941, Richland, WA 99352 (email finfrock@ambinet.com).
SPECTRUM 2000, Chattanooga, Tennessee, Sept. 24-28, 2000. Contact: SPECTRUM 2000, University of Tennessee, Department of Nuclear Engineering, Knoxville, TN 37996-2300 (phone 865-974-5048, fax 419-828-4819, email spectrum2000@engr.utk.edu, url http://www.engr.utk.edu/spectrum/).
ICENES 2000, The 10th International Conference on Emerging Nuclear Energy Systems, Sept. 25-28, 2000, Petten, The Netherlands. Contact: Mrs. M. Hofman, Meeting Secretariat, NRG, P.O. Box 25, 1755 ZG Petten, The Netherlands (phone +31-224-56-4193, fax +31-224-56-3490, email hofman@nrg-nl.com, url http://www.nrg-nl.com/congres/icenes/).
October 2000
YUNSC 2000, Oct 2-5, 2000, Belgrade, Yugoslavia. Contact: Radojko Pavlovi, YUNSC 2000 Conference Secretary, The VINCA Institute of Nuclear Sciences, P.O.B. 522, 11001 Belgrade, Yugoslavia (phone + 381-11-453-867, fax + 381-11-455-943, email yuns@rt270.vin.bg.ac.yu).
6th Annual Workshop on Monte Carlo Simulation of Radiotherapy Treatment Sources Using the OMEGA/BEAM Code System, Oct. 2-5, 2000, Ottawa, Canada. Contact: Blake Walters, Ionizing Radiation Standards, National Research Council of Canada, Ottawa, Canada, K1A 0R6. (phone 613-993-2715, fax 613-952-9865, email bwalters@irs.phy.nrc.ca, url www.irs.inms.nrc.ca/inms/irs/BEAM/beamhome.html).
MCNP and Visual Editor Training Course, Oct. 9-12, 2000, Richland, Washington. Contact: Randy Schwarz, MS K8-34, P. O. Box 999, Richland, WA 99352 (509-372-4042, fax 509-372-6421, email randy.schwarz@pnl.gov, url http://www.pnl.gov/eshs/software/ved.html).
2000 American Nuclear Society 14th Topical Meeting on the Technology of Fusion Energy, Oct. 15-19, 2000, Park City, Utah. Contact: url http://www.ambinet.com/ans/rps2000.htm.
4th International Workshop on Dosimetry for Radiation Processing, Oct. 22-27, 2000, San Diego, California. Contact: Dr. Harry Farrar IV, ASTM Committee E-10, 18 Flintlock Lane, Bell Canyon, CA 91307-1127 (phone 818-340-1227, fax 818-340-2132, email hfarrar4@aol.com).
International Conference on Advanced Monte Carlo for Radiation Physics, Particle Transport Simulation and Applications (MC2000), Oct. 23-26, 2000, Lisbon, Portugal. Contact: Intituto Tecnológico e Nuclear, MC2000 Conference Secretariat, Estrada Nacional 10, P-2686-953 Sacavem, Portugal (phone +351-21-994 60 00 ext. 6154, fax +351-21-994 10 39, email mc2000@itn1.itn.pt, or Dr. Pedro Vaz, Technical and Scientific Program Co-ordinator at email vaz@nea.fr, url http://lipulsi.lip.pt/mc2000/).
November 2000
5th Radiation Physics Conference--Atomic Energy, Radiation Protection, Challenges and Strategies, Nov. 5-9, 2000, Cairo, Egypt. Contact: Prof. Mohammad A. Gomaa, Atomic Energy Authority, 3 Ahmad Al-Zomor St., Alzohour District, Nasr City, Children Village Post Office, Postal Code 11787, Cairo, Egypt (fax 00202-287603, email ruatom@rusys.EG.net).
MARCH ACCESSION OF LITERATURE
The following literature cited has been reviewed and placed in the RSICC Information Storage and Retrieval Information System (SARIS), now searchable on the RSICC web server (http://www-rsicc.ornl.gov/SARIS.html). This early announcement is made as a service to the shielding community. Copies of the literature are not distributed by RSICC. They may generally be obtained from the author or from a documentation center such as the National Technical Information Service (NTIS), Department of Commerce, Springfield, Virginia 22161. For literature listed as available from INIS contact INIS Clearinghouse, International Atomic Energy Agency, P.O. Box 100, A-1400 Vienna.
Radiation Shielding Literature
NUREG/CR-6665; ORNL/TM-1999/303 . . . Review and Prioritization of Technical Issues Related to Burnup Credit for LWR Fuel. . . . Parks, C.V.; DeHart, M.D.; Wagner, J.C. . . . February 2000 . . . Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN; U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission, Washington, DC.
ORNL/TM-1999/246 . . . Review of Axial Burnup Distribution Considerations for Burnup Credit Calculations. . . . Wagner, J.C.; DeHart, M.D. . . . March 2000 . . . Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN.
ORNL/TM-1999/247 . . . SCALE-4 Analysis of LaSalle Unit 1 BWR Commercial Reactor Critical Configurations. . . . Gauld, I.C. . . . March 2000 . . . Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN.
ORNL/TM-13723 . . . Review of ENDF/B-VI Fission-Product Cross Sections. . . . Wright, R.Q.; MacFarlane, R.E. . . . Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN; Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, NM.
ICRU REPORT 62 . . . Prescribing, Recording and Reporting Photon Beam Therapy (Supplement to ICRU Report 50). . . . November 1999 . . . International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements, Bethesda, MD.
Book . . . Review of Monte Carlo and Deterministic Codes in Radiation Protection and Dosimetry. . . . Tagziria, H., ed. . . . February 2000 . . . National Physical Laboratory, Middlesex, UK.
INDC(SUD)-004 . . . On the Systematics of the (n,2n) Reaction Cross-Sections at 14.5 MeV Neutrons. . . . Osman, K.T.; Habbani, F.I. . . . February 2000 . . . IAEA Nuclear Data Section, Vienna, Austria.
Nucl. Technol., 129, 141-151 . . . Boiling Water Reactor Fuel Behavior Under Reactivity-Initiated-Accident Conditions at Burnup of 41 to 45 GWd/tonne U. . . . Nakamura, T.; Yoshinaga, M.; Takahashi, M.; Okonogi, K.; Ishijima, K. . . . February 2000 . . . Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute, Ibaraki-ken, Japan;Toshiba Corp. Isogo-ku, Yokohama, Japan.
Nucl. Technol., 129, 175-186 . . . A Personal Computer-Based Simulator for Nuclear-Heating Reactors. . . . Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, D.; Shi, Z.; Chen, X.; Dong, Y. . . . February 2000 . . . Tsinghua University, Beijing, China.
Nucl. Technol., 129, 201-217 . . . Validation of the Vitamin-B6 and Bugle-96 Cross-Section Libraries for Moderate-Energy Neutron and Photon Transport Calculations. . . . Slater, C.O.; Hunter, H.T. . . . February 2000 . . . Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN.
Nucl. Technol., 129, 257-278 . . . Neutron Beam Optimization for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy Using the D-D and D-T High-Energy Neutron Sources. . . . Verbeke, J.M.; Vujic, J.L.; Leung, K-N. . . . February 2000 . . . University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, CA; Ernest Orlando Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA.
Nucl. Technol., 130, 1-8 . . . A Pin Power Reconstruction Method for CANDU Reactor Cores Based on Coarse-Mesh Finite Difference Calculations. . . . Lee, H.S.; Yang, W.S.; Na. M.G.; Choi, H. . . . April 2000 . . . Chosun University, Kwangju, Korea; Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute, Taejon, Korea.
Nucl. Technol., 130, 9-17 . . . Fission Gas Release From UO 2+x In Defective Fuel Rods. . . . Kim, Y.S. . . . April 2000 . . . Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, IL.
Nucl. Technol., 130, 71-88 . . . Analysis of Radionuclide Release from Spent Ion-Exchange Resins. . . . Su, S-I.; Yim, M-S. . . . April 2000 . . . North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC.
Nucl. Technol., 130, 89-98 . . . Alternatives to High-Level Waste Vitrification: The Need for Common Sense. . . . Bell, J.T. . . . April 2000 . . . Bell Consultants, Kingston, TN.